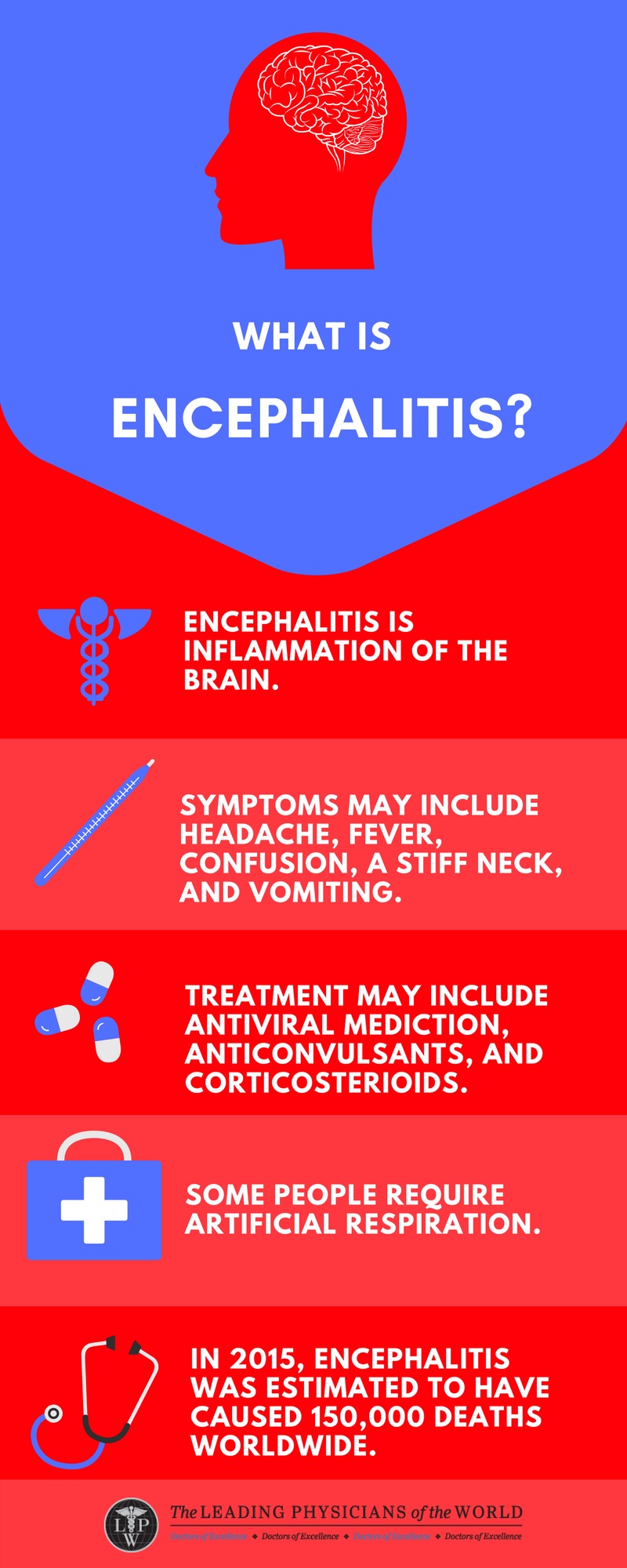
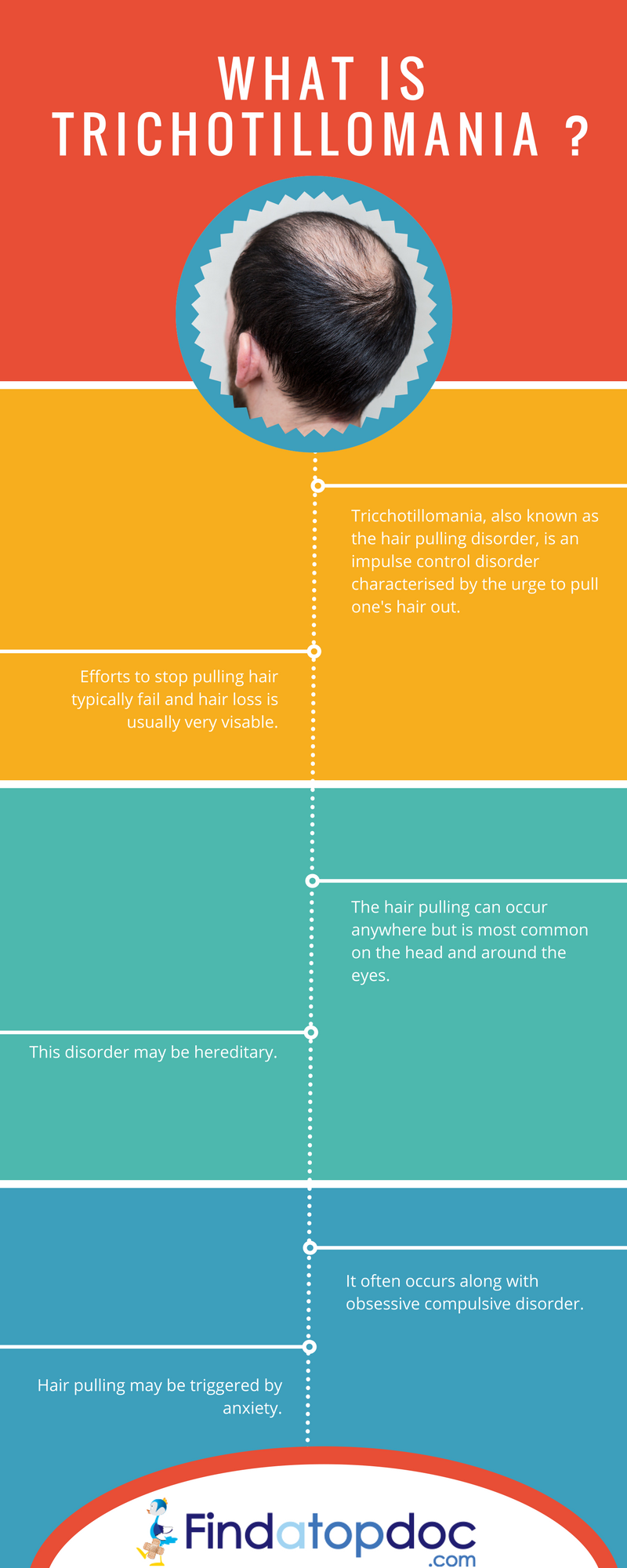
Source
Symptoms
Because of the mass of inflammatory cells in rheumatoid arthritis, the joint appears swollen and feels puffy to the touch. The increased blood flow that is a feature of the inflammation makes the joint warm.
- The joint remains swollen and "spongy" even after treatment.
- There is usually no pain or loss of motion unless there is an active bleed.
- There is an increased number of bleeds in the same joint.
The pain caused by synovitis can be a major problem in connection with other illnesses such as juvenile arthritis, lupus, and psoriatic arthritis. Synovitis can also be part of rheumatic fever, tuberculosis, injury, or gout. It is a defining characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis. In that disorder, the cells in the inflamed membrane attract other inflamed cells from all over the body, making the synovitis more and more painful. Sometimes it is not known what is causing the synovitis; a person may have had an injury that seemed minor at the time, or they may not recall an injury at all, but the fluid collects in response to the trauma and causes inflammation.