The
tibia is a large bone located in the lower front portion of the leg. The tibia is also known as the shinbone, and is the second largest bone in the body. There are two bones in the shin area: the tibia and fibula, or calf bone. The fibula is smaller and thinner than the tibia. These two bones connect the ankle to the knee and work together to stabilize the ankle and provide support to the muscles of the lower leg; however, the
tibia carries a significant portion of the body weight.
 Source
Causes
Source
Causes
High-energy collisions, such as an automobile or motorcycle crash, are common causes of tibial shaft fractures. In cases like these, the bone can be broken into several pieces. Sports injuries, such as a fall while skiing or running into another player during soccer, are lower-energy injuries that can cause tibial shaft fractures. These fractures are typically caused by a twisting force and result in an oblique or spiral type of fracture.
Symptoms
The most common symptoms of a tibial shaft fracture are:
- Pain
- Inability to walk or bear weight on the leg
- Deformity or instability of the leg
- Bone "tenting" the skin or protruding through a break in the skin
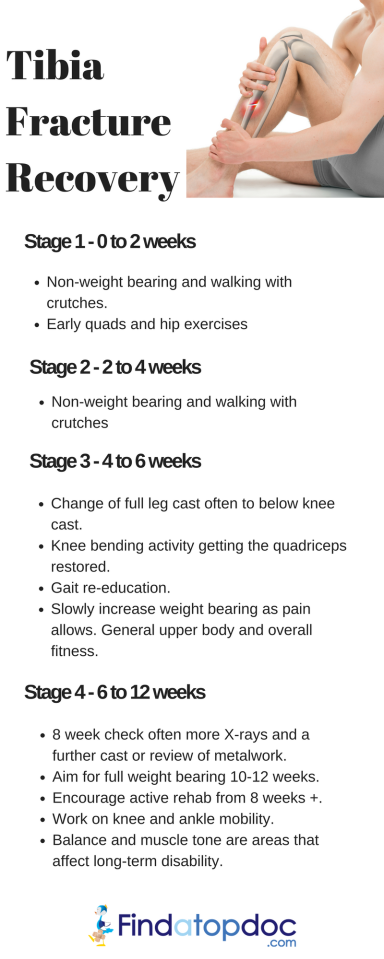
How long it takes to return to daily activities varies with different types of fractures. Some tibial shaft fractures heal within 4 months, yet many may take 6 months or longer to heal. This is particularly true with open fractures and fractures in patients who are less healthy. Pain after an injury or surgery is a natural part of the healing process. Your doctor and nurses will work to reduce your pain, which can help you recover faster.
