Source
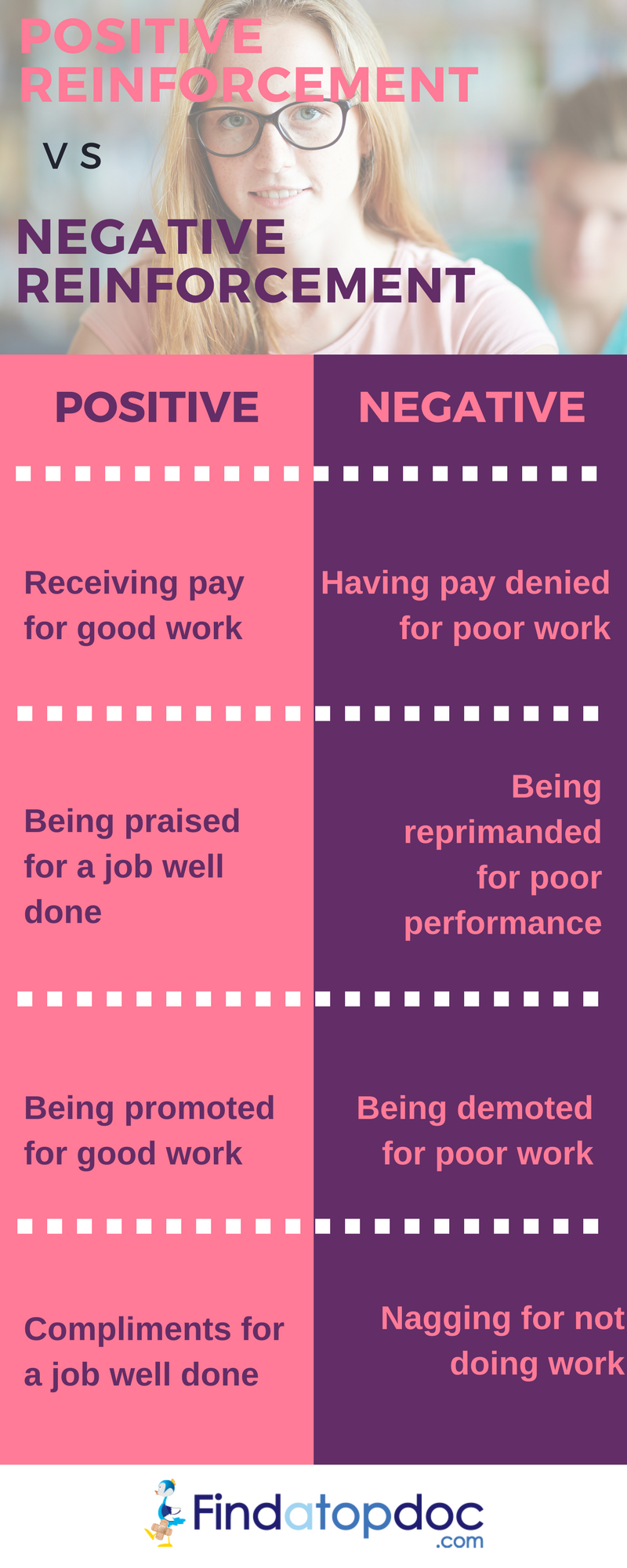
What’s the “Positive” in Positive Reinforcement?
The term “positive” is used in conjunction with reinforcement to denote a specific form of reinforcement. It does not mean something “good” but instead the term positive relates more to the mathematical term of “adding”. This is because positive reinforcement is the addition of something as a result of a behavior. Before you engaged in the behavior, what you wanted was not present but after you engaged in the behavior what you wanted is present.
Different Types of Positive Reinforces
There are many different types of reinforces that can be used to increase behaviors, but it is important to note that the type of reinforce used depends on upon the individual and the situation. While gold stars and tokens might be very effective reinforcement for a second-grader, they are not going to have the same effect on a high school or college student.
Natural reinforcers are those that occur directly as a result of the behavior. For example, a girl studies hard, she pays attention in class, and she does her homework. As a result, she gets excellent grades.When Is Positive Reinforcement Most Effective?
When used correctly, positive reinforcement can be very effective. According to a behavioral guidelines checklist published by Utah State University, positive reinforcement is most effective when it occurs immediately after the behavior. The guidelines also recommend the reinforcement should be presented enthusiastically and should occur frequently. The shorter the amount of time between a behavior and presenting positive reinforcement, the stronger the connection will be. If a long period elapses between the behavior and the reinforcement, the weaker the connection will be. These schedules of reinforcement can have a powerful influence on how strongly a response is and how often it occurs.